-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



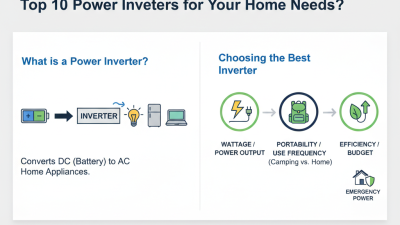
In the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions, Backup Inverters play a vital role. These devices ensure your home remains powered during outages. As we move towards 2026, the demand for reliable Backup Inverters is likely to grow.
Choosing the right Backup Inverter can feel overwhelming. There are numerous options available, each with distinct features. Some may not meet your specific needs, leading to frustration. It's essential to consider factors such as capacity and efficiency. Mistakes can lead to wasted energy and money.
Staying informed about the best Backup Inverter options is crucial. You'll want to invest wisely for long-term benefits. Look for brands that emphasize reliability and user-friendly interfaces. Remember, the right choice can enhance your energy independence.

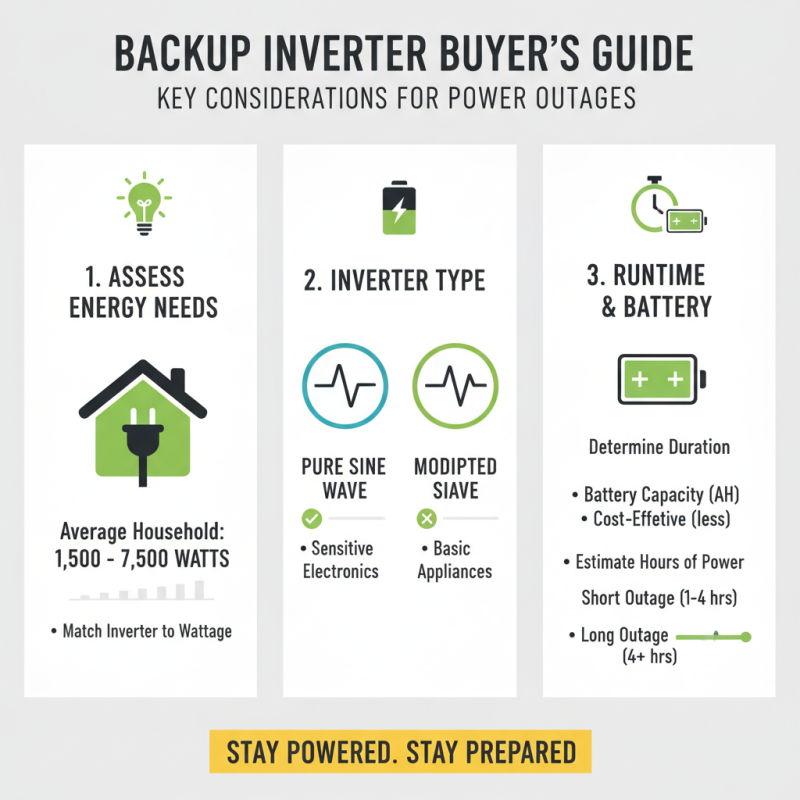
Choosing the right backup inverter is crucial for anyone concerned about power outages. Several factors should be considered. First, assess your energy needs. According to a 2022 industry report, the average household requires around 1,500 to 7,500 watts during a blackout. Knowing your wattage requirements helps in selecting a suitable inverter.
Another important factor is the inverter type. There are pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters provide cleaner power, which is more compatible with sensitive electronics. However, they can be pricier. In contrast, modified sine wave inverters are often cheaper but can cause issues with some devices. The choice should depend on your appliances and their sensitivity to power quality.
Battery compatibility is another consideration. Inverters vary in the types of batteries they support. Some models work best with lithium-ion batteries, while others may favor lead-acid batteries. Each type has its own lifespan and efficiency. A 2023 report indicates that lithium-ion batteries can last up to 10 years longer than lead-acid options. Weighing these details carefully can help avoid costly mistakes. Select a backup inverter that aligns with both your current and future energy needs.

When choosing a backup inverter, understanding the types available is essential. There are several primary types, including pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and grid-tie inverters. Each type has distinct benefits based on your specific energy needs. Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for sensitive electronics. They provide clean and stable power, making them suitable for home appliances.
Modified sine wave inverters, while more affordable, can be less efficient for complex devices. They work fine for basic applications, but you might face compatibility issues with some electronics. Grid-tie inverters excel in maximizing energy from renewable sources. They convert DC power into AC power and feed it back into the grid. This is beneficial for homeowners looking to reduce energy costs.
Consider your energy consumption patterns. If you frequently use high-power devices, opt for a pure sine wave inverter. It’s not just about initial costs; think long-term efficiency and reliability. Choose wisely based on your energy habits. Sometimes, the cheaper option can lead to higher costs later due to inefficiency or damage to appliances.
When choosing a backup inverter, certain features can make a significant difference. Look for inverters with a high efficiency rating. Efficient models convert more energy, reducing waste and maximizing power output. Also, check the power capacity. This ensures the inverter can handle your essential devices during an outage.
Battery compatibility is crucial. Inverters need to work well with various battery types. Lithium batteries are lightweight and charge quickly, which can be beneficial. Consider having additional battery backups for extended outages. Also, review the inverter's surge capacity. This peak power rating affects how many and what devices you can run simultaneously.
Tips: Always read user reviews. Real-life experiences provide insights that specifications may not cover. Think about your specific needs. Do you require a model for home appliances, or is portability more important? Understanding these details helps you make a better choice.
When considering backup inverters for 2026, several factors come into play. The efficiency of each option is crucial. Look for models that convert DC to AC power without significant loss. Some units claim high efficiency, but real-world performance may vary. Testing each product under load can reveal discrepancies in the specifications.
Accessibility of features is another key aspect. User-friendly interfaces make a big difference, especially in emergencies. Consider inverters that offer remote monitoring and control. However, these advanced features may come at a higher price. Sometimes, simpler models perform just as well without the bells and whistles. Reflect on your actual energy needs before making a decision.
Reliability is paramount for backup systems. Research shows that some brands frequently underperform during outages. Their efficacy can diminish over time if maintenance is neglected. It is essential to assess warranty conditions. Some products offer extensive coverage, while others fall short. Take these considerations seriously to avoid future inconveniences.
When budgeting for a backup inverter, consider various factors. The initial cost is just the tip of the iceberg. You must also account for installation fees. Hiring professionals adds to your budget. Alternatively, you could attempt a DIY installation, but that presents its own challenges. Mistakes can lead to added expenses.
Next, think about maintenance costs. These inverters require regular check-ups. Ignoring these needs might lead to larger repairs later. It’s crucial to set aside funds for unexpected issues. A good practice is to allocate 10-15% of the initial cost annually for maintenance.
Finally, evaluate energy efficiency. Sometimes, a cheaper inverter offers poor performance. Higher efficiency can lead to savings on energy bills. It’s worth looking at long-term costs. Short-term savings might not always be the best option. Carefully reviewing these aspects can guide your financial planning.
| Type | Power Output (W) | Battery Type | Cost ($) | Estimated Runtime (Hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Sine Wave | 3000 | Lithium-ion | 1200 | 5 |
| Modified Sine Wave | 1500 | Lead-acid | 600 | 3 |
| Hybrid Inverter | 5000 | Lithium-ion | 1500 | 8 |
| High Capacity Inverter | 6000 | Lead-acid | 1800 | 10 |
| Portable Inverter | 1000 | Lithium-ion | 400 | 2 |