
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



In today’s fast-paced world, ensuring a reliable power supply is crucial for both residential and commercial applications. A Voltage Inverter plays a vital role in converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), thereby facilitating the use of battery-stored energy to power various devices. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in energy systems, “Understanding how a Voltage Inverter works is essential for optimizing your energy efficiency and reducing costs.”
The functionality of a Voltage Inverter is not only significant for those seeking sustainable energy solutions but also for anyone who simply needs to keep their devices operational during power outages. With advances in technology, these devices have become more efficient and accessible, making them a popular choice for both off-grid living and backup power systems. This article will explore the principles behind Voltage Inverters, how they operate, and their importance in meeting contemporary power demands. By diving into the workings of these essential tools, we can better appreciate their role in our daily lives and the broader energy landscape.
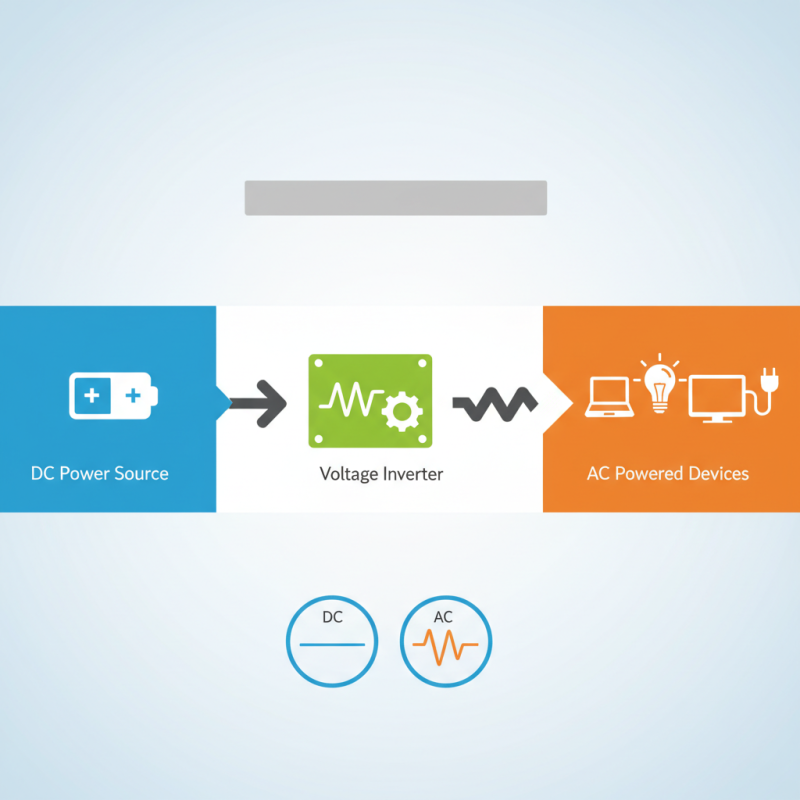
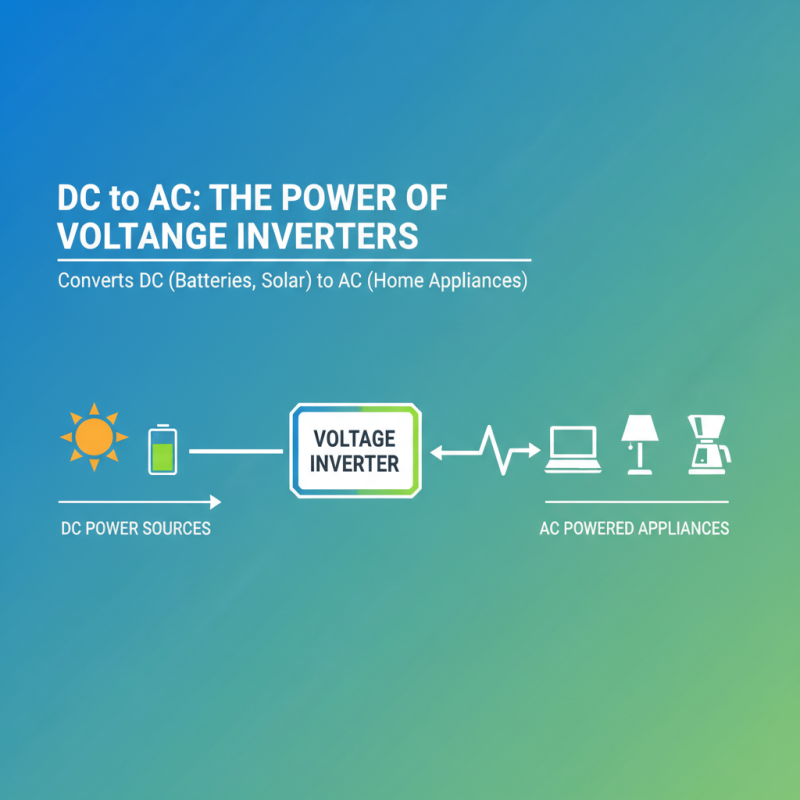
A voltage inverter, often referred to as a power inverter, is an essential device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion is crucial because many household appliances and electronic devices operate on AC power, while batteries, solar panels, and other renewable energy sources typically produce DC power. By bridging the gap between these two types of current, voltage inverters allow for the efficient use of energy stored in batteries or generated from renewable sources.
The operation of a voltage inverter relies on specific electronic components and circuitry designed to alter the voltage and frequency of the input current. Generally, a voltage inverter takes the DC input and processes it through switching elements that rapidly turn the current on and off, creating a waveform. This waveform is then modified to produce a clean, usable AC output that can supply power to various devices. Inverters can range in size and capability, from small models designed for use in mobile applications to larger systems intended for home solar power setups, making them versatile tools for various energy needs.
Voltage inverters, also known as DC to AC converters, are devices that transform direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). This conversion is essential for a variety of applications, especially in empowering household appliances and electronic devices that typically operate on AC. The fundamental principle behind a voltage inverter's operation revolves around switching components that alternate the direction of current flow. By rapidly switching the voltage polarity, the inverter generates a waveform resembling AC electricity.
Inverters generally employ components such as transistors or thyristors to control the switching process. A common architecture uses pulse-width modulation (PWM) to regulate the output voltage and frequency. This method involves adjusting the width of the pulses in relation to the total cycle duration, allowing for fine-tuning of the output signal. As a result, the inverter can provide a stable voltage output suitable for various devices, ensuring they receive the correct power supply for optimal performance. This operational flexibility makes voltage inverters a critical component in renewable energy systems, uninterruptible power supplies, and many everyday electrical applications.
When it comes to voltage inverters, understanding the various types available and their applications is crucial for optimizing your power needs. There are several common types of voltage inverters, including pure sine wave, modified sine wave, and square wave inverters. Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, clean power output, making them ideal for sensitive electronic devices, while modified sine wave inverters are more versatile and suitable for a wider range of applications at a lower cost. Square wave inverters, though outdated, can still be useful for simple devices and tools that don't require high-quality power.
Tips: When choosing a voltage inverter, consider the types of devices you'll be powering. If you're running sensitive electronics, it’s worth investing in a pure sine wave inverter to avoid potential damage. For general-purpose applications where cost is a factor, a modified sine wave inverter might suffice. Additionally, it's essential to ensure that the inverter's output wattage meets or exceeds the cumulative wattage requirement of all connected appliances.
Another essential type to consider is the grid-tie inverter, which connects your renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, back to the utility grid. This type allows for seamless integration and may even enable compensation for excess energy produced. In contrast, off-grid inverters are designed for standalone systems that require battery backup, making them optimal for remote locations or emergency power solutions. Understanding these distinctions will guide you in selecting the right inverter for your specific energy needs.
Voltage inverters are essential devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), making them invaluable for a variety of power needs. One of the primary benefits of using voltage inverters is their ability to provide power to appliances that require AC input. This is particularly useful in situations where only DC power sources, such as batteries or solar panels, are available. By facilitating the use of various electronic devices, voltage inverters expand the potential for off-grid living and renewable energy applications.
Another significant advantage of voltage inverters is their adaptability. They come in various sizes and capacities, enabling users to select the right model based on their energy requirements. Whether powering small devices or larger systems, inverters can efficiently manage energy distribution. This flexibility not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to energy savings, allowing for effective management of power consumption. Overall, voltage inverters play a crucial role in optimizing energy use, making them a smart choice for individuals and businesses looking to reduce energy costs and promote sustainability.
When choosing a voltage inverter for your power needs, several key factors should be considered to ensure you select the right unit. First, it's essential to determine the inverter's power output capacity, usually measured in watts. This capacity should align with the total wattage of the devices you intend to connect. It's advisable to add about 20% to your calculated requirements to accommodate potential surges in power demand when appliances start up.
Another critical factor is the type of inverter technology: modified sine wave versus pure sine wave. Modified sine wave inverters are generally more affordable and suitable for simpler devices, while pure sine wave inverters provide cleaner power, making them ideal for sensitive electronics like laptops and medical equipment. Additionally, the inverter's efficiency rating plays a significant role in energy consumption, so aim for an inverter with a high efficiency to minimize energy losses during operation.
Lastly, consider the inverter's size, weight, and portability features, especially if you need to use it in various locations or during outdoor activities. A compact and lightweight model may be beneficial for mobility, but ensure it doesn’t compromise on capacity and performance. Lastly, evaluate features like built-in protection mechanisms for overloading, overheating, and short circuits, which contribute to the overall safety and reliability of the inverter.
| Key Factor | Description | Specifications | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | The voltage level required to power the inverter | 12V, 24V, 48V | Choose based on the power source |
| Output Voltage | The voltage level supplied to electrical devices | 110V, 220V | Check device compatibility |
| Power Rating | Maximum load the inverter can handle | 300W, 500W, 1000W | Match power rating to equipment needs |
| Efficiency | The ratio of output power to input power | 85% - 95% | Higher efficiency reduces energy loss |
| Waveform Type | Type of electrical waveform produced | Modified Sine Wave, Pure Sine Wave | Pure sine wave is suited for sensitive electronics |
| Cooling System | Method used to prevent overheating | Fan-Cooled, Passive Cooling | Ensure adequate ventilation |





